5 Important Parts of the Engine of Old Cars and Their Functions
The car engine is often referred to as the beating heart of a car, and rightfully so. It plays a crucial role in the overall performance of the vehicle. Comprising various components, each with its specific function, the engine is a complex system that allows the car to generate power and move forward. In this article, we will explore the five important parts of the engine in old cars and their functions in detail.
Cylinder Block: The Foundation of the Engine
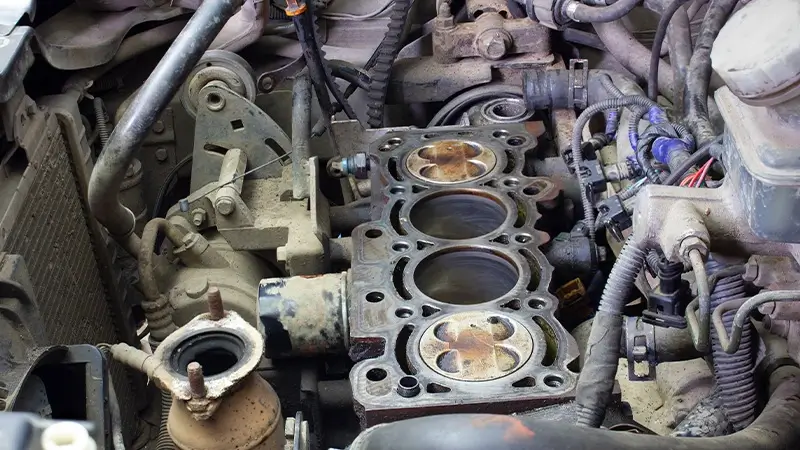
The cylinder block is the engine’s main body, forming its foundation. This integral part houses several components, including cylinders, connecting rods, crankshafts, pistons, cylinder heads, cartels, and rings. It is within the cylinder block that the combustion and sparking processes occur. Due to the high levels of heat generated, the cylinder block is typically constructed using alloys like cast iron or aluminium, which possess excellent heat resistance properties.

The primary function of the cylinder block is to facilitate the assembly of the piston, connecting rod, and crankshaft in a precise arrangement. Additionally, it serves as the site where combustion takes place, working in conjunction with other engine components.
Cylinder: Power Unit of the Engine
The cylinder is a crucial component of an internal combustion engine, playing a vital role in generating power for various types of vehicles. It can be visualized as a cylindrical chamber located within the engine’s cylinder block, where the pistons reciprocate. Often referred to as the heart of the engine, the cylinder serves as the primary site where the conversion of fuel into mechanical energy takes place, leading to the propulsion of the vehicle.
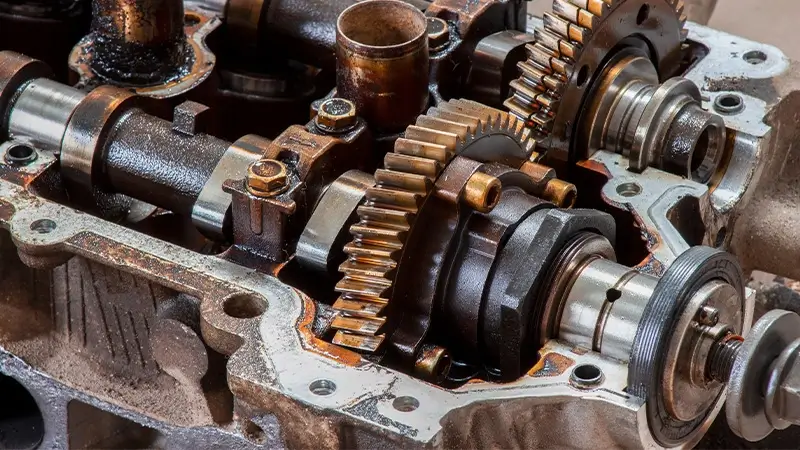

The primary function of the cylinder is to house the piston and provide the necessary space for the combustion process to occur. When the engine is in operation, the piston moves up and down within the cylinder due to the combustion forces, converting the chemical energy stored in the fuel into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then transmitted to the crankshaft through a connecting rod, which ultimately drives the vehicle’s wheels.
The number of cylinders in an engine can vary depending on the specific design and purpose of the vehicle. Typically, automotive engines feature cylinder configurations ranging from 4 to 8 cylinders, although engines with fewer or more cylinders can also be found in certain applications. Each cylinder operates synchronously with the others, allowing for smoother and more balanced power delivery.
Engines with more cylinders often offer enhanced power output and performance capabilities. This is because the presence of additional cylinders allows for more even distribution of power throughout the engine’s rotation. The firing sequence of the cylinders is usually optimized to ensure a continuous and balanced power delivery, minimizing vibrations and maximizing overall efficiency.
The size and displacement of the cylinders also play a significant role in determining an engine’s characteristics. Larger cylinders generally provide more power and torque, as they can accommodate larger pistons and a greater fuel-air mixture. On the other hand, smaller cylinders are typically more fuel-efficient and can contribute to a lighter and more compact engine design.
The materials used in manufacturing cylinders have evolved over time to withstand the high temperatures and pressures generated during combustion. Most modern engines employ cylinders made from durable cast iron or lightweight aluminium alloys, which offer excellent heat dissipation and structural integrity.
In addition to converting fuel into mechanical energy, cylinders also contribute to other engine operations. They assist in the intake and exhaust processes, allowing air-fuel mixture intake during the intake stroke and facilitating the expulsion of exhaust gases during the exhaust stroke. Proper cylinder sealing is essential to maintain efficient compression and prevent the loss of power.
Cylinder Head: The Guardian of Combustion
The cylinder head is securely fastened to the cylinder, effectively sealing the upper surface of the cylinder. This component houses essential elements such as the combustion chamber, exhaust and intake valves, and spark plugs. It also incorporates water and oil heaters, which play a crucial role in maintaining the engine’s temperature. The cylinder head can be categorized into various types, including single cylinder heads with water or air cooling and multiple cylinder heads.
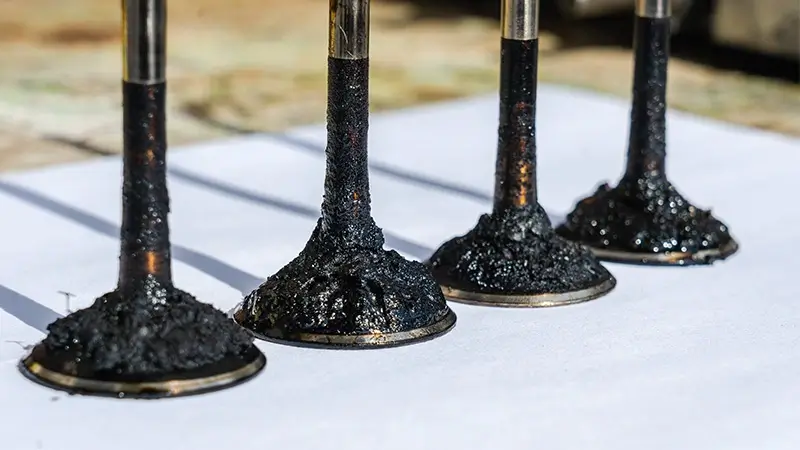

In addition to sealing the combustion chamber, the cylinder head ensures the proper injection of fuel into the cylinder and facilitates the efficient expulsion of smoke from the combustion process.
Piston: Engine’s Moving Force
The piston is a dynamic component situated inside the cylinder. Through its vertical movement, the piston completes the combustion and sparking processes while expanding the combustion gases. Pistons are commonly manufactured using materials such as cast iron, steel, or aluminium. Aluminium pistons, in particular, offer enhanced performance characteristics. The energy generated from the expanded gases is transferred to the crankshaft via the connecting rod.
In an internal combustion engine, the piston serves as a power producer. If you observe excessive oil consumption or notice white smoke emanating from the exhaust, it may indicate a failure of the piston rings. Acting as a robust metal plate, the piston compresses the gas within the cylinders.
Spark Plugs: Igniting the Engine
Spark plugs hold a pivotal role in starting the car. When you turn the key in the ignition, the electric current from the car’s battery ignites the spark plug, initiating the combustion process. Therefore, if you encounter difficulties while starting your car, it is crucial to inspect the spark plugs and promptly replace them if necessary. The cost of spark plugs can vary in different regions, with prices in Australia starting at around $10.
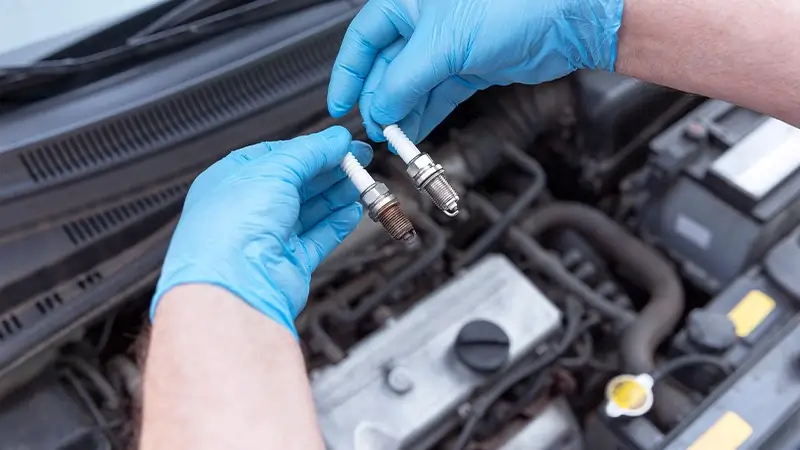

Based on their thermal rating, spark plugs come in various types, classified as cold, semi-warm, or hot. The selection of the appropriate spark plug is crucial for optimal engine performance and ignition reliability.
In conclusion, the car engine stands as a vital component, often referred to as the vehicle’s beating heart. Composed of numerous components, each serving a crucial role. The culmination of these parts allows for smooth driving and optimal performance. The five parts discussed in this article – the cylinder block, cylinder, cylinder head, piston, and spark plugs – are essential components of an old car’s engine. A malfunction in any of these parts can significantly impact the vehicle’s operation, making driving challenging. Therefore, if you want to get rid of old car for top dollar, check our cash for car or car removal for more.



